Difference between revisions of "IDE architecture design"
From stgo
(→Pro & Contra) |
|||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
== Pro & Contra == | == Pro & Contra == | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" border="1" | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | !width="250"|criteria | |
| − | + | !width="250"|single DB | |
| − | + | !width="250"|multi DBs | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | | server needs (registry server, web server, base-db server) | |
| − | + | | 2 servers (1 web server, one db server) | |
| − | + | | 1 web server, many db-servers | |
| + | |- | ||
| + | | maintenance needs (adding data, metadata, software updates) | ||
| + | | one admin (one update) | ||
| + | | many local admins (many updates) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | user access management | ||
| + | | one unified user rights management for all CEDEUS members (with 4 different access groups, e.g.: admin, cedeus member, invited, public) | ||
| + | | each DB admin needs to create its own user management system and needs to ensure access by other CEDEUS groups (However, a replication of user access rights is possible) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | data security (un-wanted access) | ||
| + | | one dedicated data server that can only be accessed via a gateway and by only very few users | ||
| + | | many databases with different user groups and different users per computer | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | data backups (copias d. seguridad) | ||
| + | | regular backup for only one db sever | ||
| + | | requires complex backup strategy or one backup devices at each location | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | power outages | ||
| + | | one web server and one db server in the same place are easy to "secure" with a UPS | ||
| + | | costly to provide UPS for several server locations | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | performance (serving data => scalability vs. multi-access) | ||
| + | | performance depends on server power, may be insufficient during concurrent access | ||
| + | | people will access (concurrent access is not very likely) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | geographic base-data (for maps) <br>(Well here we can also store base data on one particular assigned server) | ||
| + | | easier to provide one base-dataset | ||
| + | | same base-data on several servers? danger of inconsistencies | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | quality assurance (geogr. data + metadata) | ||
| + | | one dedicated expert to check data quality (data description, accuracy) | ||
| + | | many experts necessary | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | access documentation | ||
| + | | one document to create for accessing data | ||
| + | | many documents to read and maintain | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | data info distribution : to IDE de Chile | ||
| + | | fast to update info on data availability for IDE de Chile | ||
| + | | additional work to gather changes in data availability at different locations | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | (see also [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Federated_database_system Federated Database System] | ||
== Tipos de Usuarios == | == Tipos de Usuarios == | ||
Revision as of 17:53, 5 November 2013
>> return to Cedeus IDE
What Architectural Models exist
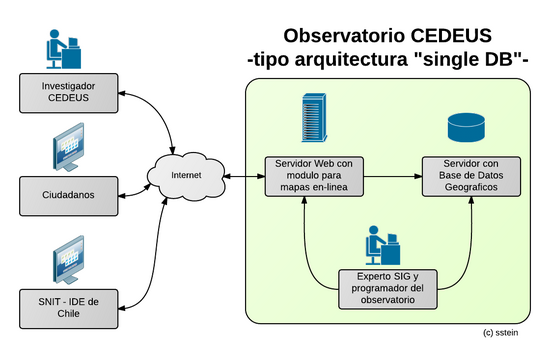
A - Central Server-Database Architecture
El imagen abajo muestra una IDE simple, con 2 servidores:
- Servidor web con modulo de mapas en-linea, y con catalogo de datos
- Servidor con base de datos
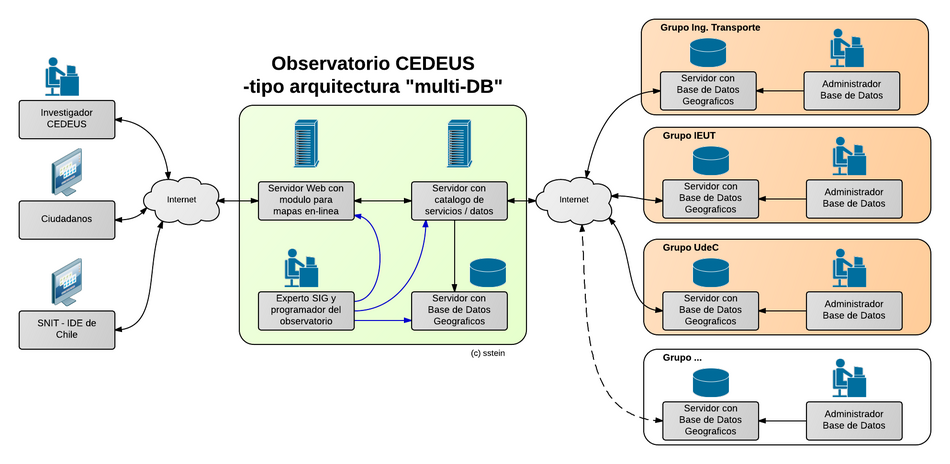
B - Distributed Multi-DB Server Architecture
El proximo imagen muestra una IDE complejo, con 6 servidores (con base de datos multiples):
- 3+ Servidores de grupos de investigacion (con BD)
- 1 Servidor de Catalogo
- 1 Servidor de Mapas
- 1 Servidor con Base de Datos (Datos Centrales)
(es posible de user un servidor con el modulo de mapas juntos con la base de datos)
Pro & Contra
| criteria | single DB | multi DBs |
|---|---|---|
| server needs (registry server, web server, base-db server) | 2 servers (1 web server, one db server) | 1 web server, many db-servers |
| maintenance needs (adding data, metadata, software updates) | one admin (one update) | many local admins (many updates) |
| user access management | one unified user rights management for all CEDEUS members (with 4 different access groups, e.g.: admin, cedeus member, invited, public) | each DB admin needs to create its own user management system and needs to ensure access by other CEDEUS groups (However, a replication of user access rights is possible) |
| data security (un-wanted access) | one dedicated data server that can only be accessed via a gateway and by only very few users | many databases with different user groups and different users per computer |
| data backups (copias d. seguridad) | regular backup for only one db sever | requires complex backup strategy or one backup devices at each location |
| power outages | one web server and one db server in the same place are easy to "secure" with a UPS | costly to provide UPS for several server locations |
| performance (serving data => scalability vs. multi-access) | performance depends on server power, may be insufficient during concurrent access | people will access (concurrent access is not very likely) |
| geographic base-data (for maps) (Well here we can also store base data on one particular assigned server) |
easier to provide one base-dataset | same base-data on several servers? danger of inconsistencies |
| quality assurance (geogr. data + metadata) | one dedicated expert to check data quality (data description, accuracy) | many experts necessary |
| access documentation | one document to create for accessing data | many documents to read and maintain |
| data info distribution : to IDE de Chile | fast to update info on data availability for IDE de Chile | additional work to gather changes in data availability at different locations |
(see also Federated Database System
Tipos de Usuarios
Tipo A - Ciudadanos
- tareas tipicos => permisos
Tipo B - Investigador CEDEUS
- tareas tipicos => permisos
Tipo C - Persona Invitado
- tareas tipicos => permisos
- accesso al unos datos especiales
Tipo D - Experto de Observatorio
- tareas tipicos => permisos
Gestion de Acceso
- al BD de datos (acceso directo: solo por expertos observatorio)
- al visor de datos (login o diferente visores: publico sin login + otro con login y interfaz diferente)
- al servicios de datos (WFS, WMS, WCS, etc)